Statistical method to evaluate the data from a designed experiment.
The size of the smallest increment on the measuring device.
Variation due to the difference in techniques in the inspection method. This is calculated as the variation to reproduce the measurements of another appraiser or inspector. Appraiser variation is referred to as “Reproducibility”.
(… of variation) Those causes of variation in a process which are not random, i.e. which have some source which can be determined and perhaps eliminated.
(Quality …) Data coming from yes/no, or pass/fail determinations of whether the units conform to standards. May or may not include weighting by seriousness of defect, etc.
Plotted curve or distribution showing a central peak and tapering off smoothly and symmetrically to “tails” on wither side. A normal curve is an example.
A condition where both an upper and lower tolerance are specified. In contrast, a unilateral distribution is one-sided. See also Unilateral distribution.
(Count – Attribute data) The count or number of events of a given classification occurring in a sample. More than one event may occur in a unit (area of opportunity), and each such event throughout the sample is counted.
(…of a data set) The ability of the process to stay within a given specification range. Capability is an evaluation function, and as such will become true or false, depending on the result of the evaluation. The actual test for capability is made by the equality: Cp>=1.0 (Cp is greater than or equal to one)
For control charts: the horizontal line marking the center of the chart, usually indicating the nominal expected value of the quality being charted.
A property which helps to differentiate between items of a given sample or population.
Shewart control charts for plotting subgroups means or variances against the control limits or Zone chart for color display of individual observations about target value.
Those sources of variability in a process which appear to be random, i.e. inherent in the process itself; these causes produce the variability within the 3 sigma limits.
(Charts) Plot of some parameter of process performance, usually determined by regular sampling of the product as a function (usually) of time or unit number or other chronological variable. The control limits are also plotted for comparison. The parameter plotted may be the mean value of a particular measurement for a product sample of specified size (x chart), the range of values in the sample (R chart), the percent of defective units in the sample (p-chart), etc.
A graphical method for evaluating whether a process is or is not in a “state of statistical control.” The determinations are made through comparison of the values of some statistical measure for an ordered series of samples or subgroups with control limits.
Limits on a control chart which are used as criteria for signaling the need for action, or for judging whether a set of data does or does not indicate a “state of statistical control.” Note: When warning limits are used, the control limits are often called action limits. Action may be in the form of investigation of the source(s) of an assignable cause, making a process adjustment, or terminating a process. Criteria other than control limits are also used frequently.
A process capability index defined only if the process is in a state of control and normally distributed. Cp tells how many process bell curves will fit into the specification range. Consequently, a value of 1.33 or greater is generally considered desirable. Cp only addresses the issue of whether the process spread is acceptable. It does not address the issue of whether the location of the process center is acceptable.
By formula, Cp = specification range / 6 sigma. Where sigma = Rbar/d2
A process capability index defined only if the process is in a state of control, is normally distributed, and has a target at the midpoint of the specification. It indicates whether the process will produce units within the tolerance limits. Cpk has a value equal to Cp if the process is centered on the mean specification; if Cpk is negative, the process mean is outside the specification limits; if Cpk is between 0 and 1, then some of the 6 sigma spread falls outside the tolerance limits. If Cpk is larger than 1, the 6 sigma spread is completely within the tolerance limits.
By formula, Cpk = Min (ZU, ZL)/3
Where ZU = (UTL – Xdbar)/sigma ; ZL = (Xdbar -LTL)/sigma; where sigma = Rbar/d2
A collection of interrelated data items. Specifically, the contents and structure of a number of tables with columns as fields (part_id, feature_id, etc…) and rows that contain data (manifold, bore depth, etc). The MEASURLK.DB database houses all the information necessary for data collection and receives the data once collected.
A departure of a quality characteristic from its intended level or state that occurs with a severity sufficient to cause an associated product or service not to satisfy intended normal, or reasonably foreseeable, usage requirements.
A plan to conduct tests that involves all of the prework that must be done prior to conducting any tests. Prework requirements are writing questions; data collection sheets are prepared; analysis of data is organized; and the limitations of the test are determined.
A window that can display any control chart, statistics, observations, etc.
The larger of the apparent and effective resolutions for single reading systems. Also referred to as the minimum accuracy of any given measuring device. The number of data categories is often called the “discrimination ratio” since it describes the number of classifications that can be reliably distinguished given an observed process variation.
The size of the data category when the total measurement system variation is considered.
A set of all the various values that individual observations may have and the frequency of their occurrence in the sample or population.
A Manager View that displays a Cpk bar graph of all characteristics in the current inspection run from worst case to best case.
A window that displays a bitmap background on which call outs can be placed that represent the statistical and measurement states of all characteristics in the current inspection run.
A plot of a frequency distribution in the form of rectangles whose bases are equal to the cell interval and whose areas are proportional to the frequencies.
The process of measuring, examining, testing, gaging or otherwise comparing the unit with the applicable requirements.
All data that pertains to a given inspection routine, including measurement data, for a single Run ID.
Correlation between the appraiser and the part. Appraiser differences should depend on the part being measured.
Lower Control Limit. Control limit for points plotting below the center level.
Difference in the bias values of a gage through the operating range of the gage.
A definite quantity of a product or material accumulated under conditions that are considered uniform for sampling purposes.
Lower Tolerance Limit. The lowest value of a product dimension or measurement which is acceptable. While LTL is now the preferred term, the term Lower Specification Limit, or LSL, was at one time more frequently used.
A snapshot window display that shows all characteristics of the current inspection run. Up to 16 snapshot windows can be viewed on the screen at once.
(Statistical) Average value of some variable. The mean is given by the formula: Mean = XBar = (X1 + X2 +X3 + . . . + XN) / N ,where N is the number of elements in the sample and XN are individual observation values.
The combination gage bias, repeatability, reproducibility, stability and linearity.
For an odd number of units: the middle value when all values have been arranged in order of size; for an ordered set X1, X2,. . . , X2k-1, Median = Xk. For an even number of values so arranged, the median is the average of the two middle units; for an ordered set X1, X2, …, X2k, Median = (Xk + Xk+1) / 2.
A list of available commands in an application window.
The horizontal bar at the top of an application window, immediately beneath the title bar, which lists the available menus.
A combination of two distinct populations. On control charts, a mixture may be indicated by an absence of points near the centerline.
While primarily referred to as the cathode ray device which provides the user with information on what is going on inside the computer (the “compute screen”), the term may refer to any software or hardware that observes, supervises, controls, or verifies the operations of a system.
Limits which include a stated fraction of the individuals in a population. Note: For populations with a Normal (Gaussian) Distribution, the natural process limits ordinarily will be set at 3s (where s = standard deviation). If placed around the standard level, these limits identify the boundaries which will include 99.7% of the individuals in a process that is properly centered and in a state of statistical control.
For a product whose size is of concern: the “name” of that particular dimension. For example, with specifications 20 (+2,-2), the nominal is 20; with specifications 30 (+5, 0), the nominal is 30.
A Gaussian distribution; A distribution that appears to be “bell shaped” . . . symmetric, most readings in the middle, tailing off at both ends. In most cases, a normal distribution is assumed for individuals. The Central Limit Theorem expresses the fact that the distribution of subgroup means tends toward normality regardless of the distribution of the individuals.
Remark or annotation attached to a subgroup to aid in the review of an output listing.
(Number of affected units) The total number of units (areas of opportunity) in a sample in which an event of a given classification occurs. A unit (area of opportunity) is to be counted only once even if several events of the same classification are encountered therein.
Process which exhibits a lack of statistical control or uniformity. See State of Statistical Control.
Tendency of recurring at regular intervals.
The combination of people, equipment, materials, methods, and environment that produce output — a given product or service. A process can involve any aspect of your business. A key tool for managing processes is Statistical Process Control (SPC).
After the process is in control, process capability describes what the process is capable of doing, typically in terms of the natural limits for variables data and the process average for attribute data. Capability is usually determined by performing measurements on some (or all) of the product units produced by the process. See also Cp and Cpk.
Maintaining the performance of a process at its capability level. Process control involves a range of activities such as sampling the process product, charting its performance, determining causes of any problems, and taking corrective actions.
The totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy given needs.
The operational techniques and the activities which sustain a quality of product or service that will satisfy given needs; also the use of such techniques and activities.
Control chart of the range of variation among the individual elements of a sample
Varying with no discernible order or pattern.
A measure of dispersion which is the difference between the largest observed value and the smallest observed value in a given sample. While the range is a measure of dispersion in its own right, it is sometimes used to estimate the population standard deviation, but is a biased estimator unless multiplied by the factor (1/d2) appropriate to the sample size. Formula: R = largest observation minus smallest observation. Note: Because the range tends to be inefficient, it is not recommended that ranges be used for large sample sizes. A “rule of thumb” suggests a maximum sample size of 10.
A calculation to define the mathematical relationship between two or more variables.
Variation in measurements obtained with a single gage being used several times by one appraiser while measuring a single characteristic on a single part.
Variation in the average of the measurements made by different appraisers while measuring a single characteristic on a single part using one gage.
The capability of the measurement system to detect and accurately indicate small changes of a measured characteristic.
An unique identifier for a given inspection run. Similar to a Lot Number or Job order number. Defaults to the date and time from the computer.
A group of units or observations taken from a larger collection of units or observations that serves to provide information that may be used as a basis for making a decision regarding the larger quantity.
Abbreviation for SUBGROUP.
A plot of two variables, one against the other, to display correlations.
Standard deviation (of individuals, means, ranges, etc.) See Standard Deviation.
Number of standard deviations of the variable being plotted (mean, range, etc.) used for calculating the control limits.
Manager view – A small window that displays all characteristics in an inspection routine in one of the following views: Box-Whisker, Meter chart, Histogram, Information.
Limits that define the conformance boundaries for an individual unit of a manufacturing or service operation.
Process that is in statistical control. A process is said to be stable if it shows no recognizable pattern or change.
A measure of variability (dispersion) of observations in the sample that is the positive square root of the sample variance,
standard deviation = sigma = s
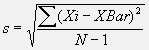
where: N = the number of data elements; Xi = the ith item in the data set;
XBar = mean or average of the data set.
A control limit calculation method which is based on adopted standard values applicable to the statistical measures plotted on the chart.
A process is considered to be in a “state of statistical control” if, in the variations among the observed sampling, the results from it can be attributed to a constant system of chance causes.
A quantity calculated from a sample of observations, most often to form an estimate of some population parameter.
(SPC) A technique used with the aid of measurements or factual data, which represents the process output characteristics; assignable causes of unpredictability are eliminated so that the process behaves in a state of statistical control.
A horizontal bar beneath a window that displays status information.
(… of a sample) If a sample is formed by combining units from several lots having different properties, the sample distribution will show a concentration or clumping about the mean value for each lot: this is called stratification. In control charting, if there are changes between subgroups due to stratification, the R-chart points will all tend to be near the centerline.
Subgroups are typically made up of consecutive pieces, although random samples are sometimes used. (Object Sense) A set of units or quantity of material obtained by subdividing a larger group of units or quantity of material. (Measurement Sense) A set of groups of observations obtained by subdividing a larger group of observations.
How many observations, events, or measurements are included in each subgroup.
Value within the specification limits which will be aimed for because it is decided that this is the best value for that quality characteristic; not necessarily either the nominal or the midpoint of the specifications.
The total allowable variation around a level or state (upper limit minus lower limit), or the maximum acceptable excursion of a characteristic.
The ability to attach concise notes at various points of an inspection run. Traceability items include; Assignable causes of variation, Operator names, Process centers, Customers and Suppliers, etc.
Gradual, systematic change with time or with another variable. Seven consecutive descending or ascending variable observations constitutes a trend.
(Count per unit) The average count, or average number of events of a given classification, per unit (unit area of opportunity) occurring within a sample. More than one event may occur in a unit, and each such event is recorded.
Upper Control Limit. Control limit for points plotting above the center level. See Control limits.
One-sided tolerance; that is, only one tolerance limit (either a minimum below the target, or a maximum above the target) is specified. In contrast, a bilateral distribution is two-sided. See also Bilateral Distribution.
Upper Tolerance Limit. The highest value of a product dimension or measurement which is acceptable. While UTL is now the preferred term, the term Upper Specification Limit, or USL, was at one time more frequently used.
The property of exhibiting variation, i.e., in particular, changes or differences in the product of a process.
Variance is a measure of dispersion. The actual formula used by the program for the calculation:
variance = ![]()
where N = the number of data elements; Xi = the ith item in the data set; Xbar = mean or average of the data set, and s = standard deviation.
Refers to a particular program’s age, the form or variation from the original program. Software is usually given a new version designation with each new release or update, the newer version typically having a higher number. For some programs, may refer to a command which reports the program’s version to the user.
Limits at which attention is called to the possibility of out-of-control conditions, but further action is not necessarily required.